For a complete publication list, please refer HERE or to my Google Scholar profile. 查询完整的论文列表请点击此链接。
Selected publications 代表性论文
4. Rational tuning of temperature sensitivity of the TRPM8 channel [EMBO Reports] (Co-first, 20251021)
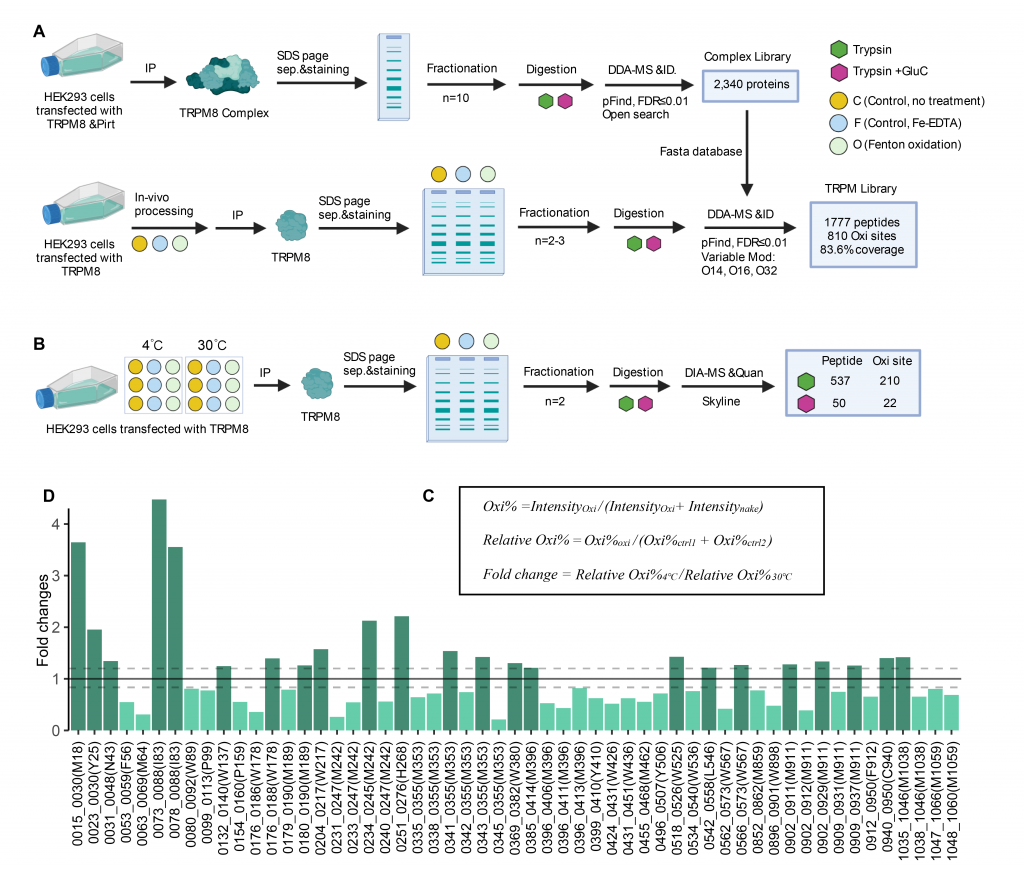
Detecting temperature is crucial for the survival of living organisms. Thermo transient receptor potential (thermoTRP) channels, such as TRPV1 or TRPM8, have been identified as prototypic heat or cold sensors, respectively. However, how they detect temperature remains elusive.
We developed hydroxyl radical footprinting-data-independent acquisition mass spectroscopy (HRF-DIA-MS), a combinative technology, to quantitatively profile the protein residues that undergo burial/exposure conformational rearrangements during temperature activation. Our findings established that the water-protein interaction is a common mechanism underlying temperature sensing in TRPM8 and TRPV1.
I contributed to the proteomic methodology and data analysis.
感受温度对于生存至关重要。我们已经知道热感和冷感感受器的蛋白对应于如 TRPV1、TRPM8等热瞬态受体通道;然而,它们检测温度的机制至今仍不清楚。
我们开发了一种“羟基自由基足迹-数据非依赖型采集质谱”(HRF-DIA-MS)的技术,用于对在温度导致的蛋白质残基的转变构象进行大规模、非偏倚的鉴定和定量分析。我们的研究结果表明,水与蛋白质的相互作用是 TRPM8 和 TRPV1 实现温度感知的常见机制。
我负责了蛋白质组学的方法开发以及相关的数据分析工作。
3. Integrative multi-omics deciphers the spatial characteristics of host-gut microbiota interactions in Crohn’s disease [Cell Reports Medicine] (Co-first, 20230620)
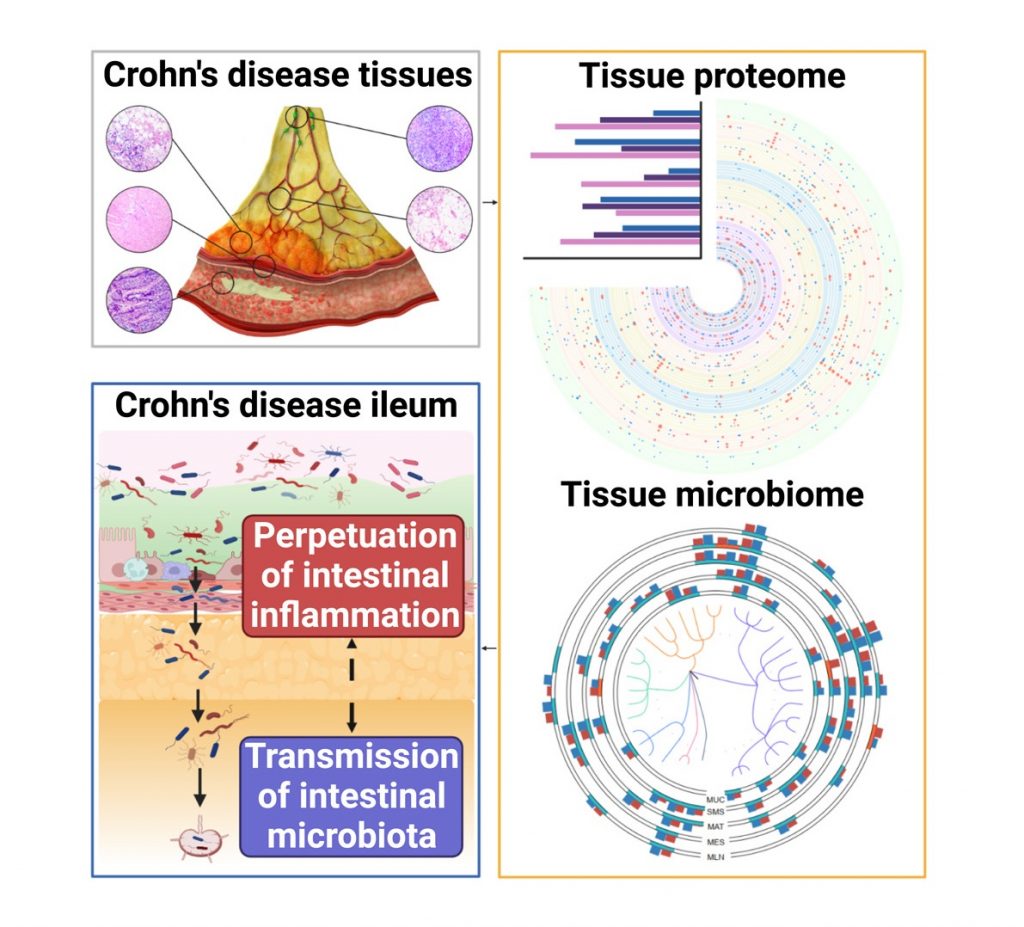
Host-microbial interactions play critical roles during gut inflammation in Crohn’s Disease (CD), a type of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
We applied proteomics and microbiomics to characterize five sections of diseased tissue from thirty CD patients, and thereby analyzed the host responses as well as their interactions with bacterium. Over 600 proteomes were analyzed in the project and we specially implemented Pulse DIA technique on a TimsTOF mass spectrometry to increase proteome depth. We proposed diagnostic biomarkers with signature alteration that are also shown in serum and feces.
I contributed to proteomic experiments, data analysis, and paper revision.
克罗恩病(CD)是一种复杂的炎症性肠病,其发病过程中,宿主与微生物之间的相互作用十分关键但其机制尚未被充分表征。
我们对 30 名 CD 患者回肠中的五处病变组织切片进行了蛋白质组和微生物组的分析。其中,蛋白质组数据基于新近开发的pulse-diaPASEF方法采集、采集总数目超过 600 个。从超过8000种蛋白结果的挖掘中,我们提炼出了一批与CD特征显著相关的诊断型生物标志物,并通过额外探索发现这些标志物也可从血清和粪便中被表征和鉴定。
我负责了蛋白质组学实验、数据分析和论文修订的工作。
2. Proteomics Investigation of Diverse Serological Patterns in COVID-19 [Molecular & Cellular Proteomics] (First, 20230105)

Our body relies heavily on the secretion of serum antibodies to defend against SARS-CoV-2 attacks. From current clinical reports, we noticed patients with unexpected serological patterns, such as negative antibody expression throughout COVID-19, and exceptionally high expression of IgM or IgG at their plateau. These observations suggest diverse host responses during COVID-19, which have yet to be assessed.
In this study, we applied two-year clinical manifestation and lop、ngitudinal serum proteomics to understand the serology in a cohort of 144 COVID-19 patients. The findings suggest that COVID-19 patients who do not express antibodies developed cellular immunity for viral defense, and that high titers of IgM might not be favorable to COVID-19 recovery.
I contributed to proteomic experiments, data analyses, and manuscript writing.
人体主要依赖血清抗体的分泌来抵御新冠病毒侵袭。但现有临床报告显示,部分患者呈现特殊的血清学特征:有的在整个病程中始终未检出抗体表达,有的则出现异常高水平的IgM或IgG平台期。这些现象提示新冠病毒感染过程中存在多样化的宿主免疫应答机制,其临床意义尚待系统评估。
本研究通过整合144名新冠患者为期两年的临床表现与纵向血清蛋白质组数据,首次揭示:未产生抗体的患者可能通过细胞免疫实现病毒防御,而高滴度IgM反而可能不利于临床康复。
我负责了蛋白质组学实验、数据解析及论文撰写工作。
Affiliated blog相关博客
1. Computational Optimization of Spectral Library Size Improves DIA-MS Proteome Coverage and Applications to 15 Tumors [Journal of Proteome Research] (Co-first, 20211108)

Public MS data repositories are being generated for proteomic studies. They provide accessible spectral information for library-based DIA-MS data analyses. However, vast number of false positives may be introduced due to an enlarged search space, leading to an unpleasant proteomic identification.
Via a two-step strategy called subLib to generate experiment-specific subset libraries from the public data, we downscaled the library size while enhanced the resultant proteomic coverages from DIA-MS data by 30-40%. This method is proven handy in proteomics of 15 tumor tissues.
I contributed to data revision and manuscript writing.
Patents 专利
- 郭天南;梁潇;朱怡. 伴随蛋白/肽在提高蛋白质组实验效率中的应用. ZL202010762585.6 (CN patent) certificate
- 郭天南;梁潇;石颖秋;王瑛睿. 一种高效清除液相色谱中多肽残留的方法及应用. ZL202210103388.2 (CN patent) certificate
- 郭天南;梁潇;陈晨;石颖秋. 一种生物样本的蛋白质组学分析方法. ZL202210399034.7 (CN patent) certificate
- 郭天南;梁潇. 一种分析细胞亚型的方法. 审核中 (CN patent pending; Pub. No. CN117309727A)